You may have heard the term “digital printing” while researching companies for printing. Many people, however, aren’t quite sure what digital printing means.
We will break it down for you so that you have a better understanding about the benefits that digital print offers as well as the differences between digital print and offset print (also referred to as analog or lithographic print).
To get things started, digital print offers many benefits that you simply cannot achieve with offset printing. The benefits of digital printing include: Faster turnaround times, the capability of smaller print runs, high quality printing while maintaining a low per unit cost, and the ability to easily provide a printed proof.
At this point, you may be asking: Wait. What is offset printing?
Offset printing printing is a commonly used technique in which the inked image is transferred (or “offset”) from a plate to a rubber blanket, then to the printing surface. The problem with offset printing is that there is very little room for error. The plates need to be created first before printing can proceed. This prevents the ability to see a printed proof first (Note: It can be done with offset, but is very costly). It also requires much larger runs to justify the creation of the plates. It does take more time to produce a print run as well.
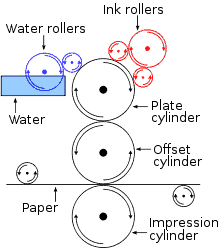
Offset Printing Diagram
Offset printing definitely has it’s place and need in the print world. Most large scale print runs, recurring publications and other things of the like benefit from the factory-like process.
However, if you are a business owner and need something printed fast, while still maintaining a high quality and want to see a printed proof before your job gets started, you will likely need to turn to digital print.
Digital printing refers to methods of printing from a digital-based image directly to a variety of media. Meaning: It goes directly from your PDF file, for instance, straight to the digital printer. There is no need to create any plates, and setup time is a fraction of the time offset printing would take.
Digital printing usually refers to professional printing where small-run jobs from desktop publishing and other digital sources are printed using large-format and/or high-volume laser (like the Xerox 800 pictured below, one of many digital printers that we use here at Replica Printing) or inkjet printers.

Xerox 800 Digital Printer
One possible drawback of digital printing, is that it has a higher cost per page than more traditional offset printing methods, but this price is usually offset (no pun intended) by avoiding the cost of all the technical steps required to make printing plates. Also, with digital, there may be a loss of some fine-image detail by most commercial digital printing processes. However, in most cases, the pros vastly outweigh the cons, and as digital printing technology progresses, the difference in print quality between digital and analog lessens.
One more benefit to digital print is that the design can be modified along the way. Since there is no permanent plate to deal with, if it turns out there is a spelling or design error on a printed proof, the file can be easily modified before the print run continues. It is very flexible that way.
The savings in labor and the increasing capability of digital machines means that digital printing is getting to a point where it can match or supplant offset printing technology’s ability to print bigger runs.
We are quickly moving into a fully digital age in every possible way, print included. Digital print is quickly evolving and technology is constantly improving.
If you own a business and need print work, digital print is most likely the way to go.